This research report was funded by Iowa Department of Agriculture and Land Stewardship and Johnny’s Selected Seeds.
In a Nutshell
- Timing the fall planting of cauliflower and other slow-maturing crops is often difficult, especially when planting a new variety. There are many varieties of cauliflower available to farmers in array of colors, plant and head sizes and average days to maturity.
- Building on several past PFI studies, a group of cooperators conducted a trial to determine the performance of seven cauliflower varieties planted as fall crops.
Key Findings
- Snow Crown was consistently high yielding and outyielded all other trialed varieties at two of three farms that tested it.
- Of the colorful varieties that cooperators tried, Cheddar generally performed the best. Lavender, the only purple variety trialed, produced minimal harvests at Hegmann & Kerns’ and Quee’s.
Background
Cooperators Natasha Hegmann & Pete Kerns, Michael Pipho, Mark Quee and Carmen and Maja Black all had questions about which cauliflower varieties they should plant for their fall crop. Building on previous PFI Cooperator research investigating this topic in 2019 [1] and 2022 [2], they performed a cauliflower variety trial in fall of 2023. Each farm tested a subset of seven cold-tolerant varieties that vary in color, plant size, and days to maturity. The cooperators hoped to use the trial to improve their production by determining the performance of the different varieties. They were also very interested in trying new varieties and gauging customer interaction. At the outset, Carmen and Maja Black said “This research trial will inform when our farm plants cauliflower and which varieties we will prioritize, with yield, diversity, and customer enjoyment (exciting colors) as factors to consider.” Quee added: “figuring out start dates for fall-harvested crops is often challenging and this trial will hopefully help us improve at that.”
Methods
Design
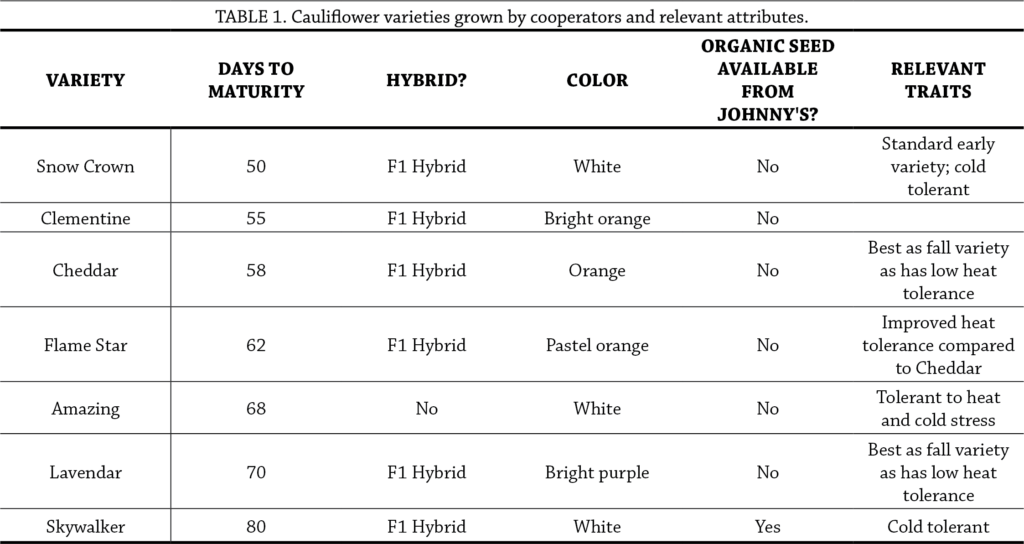
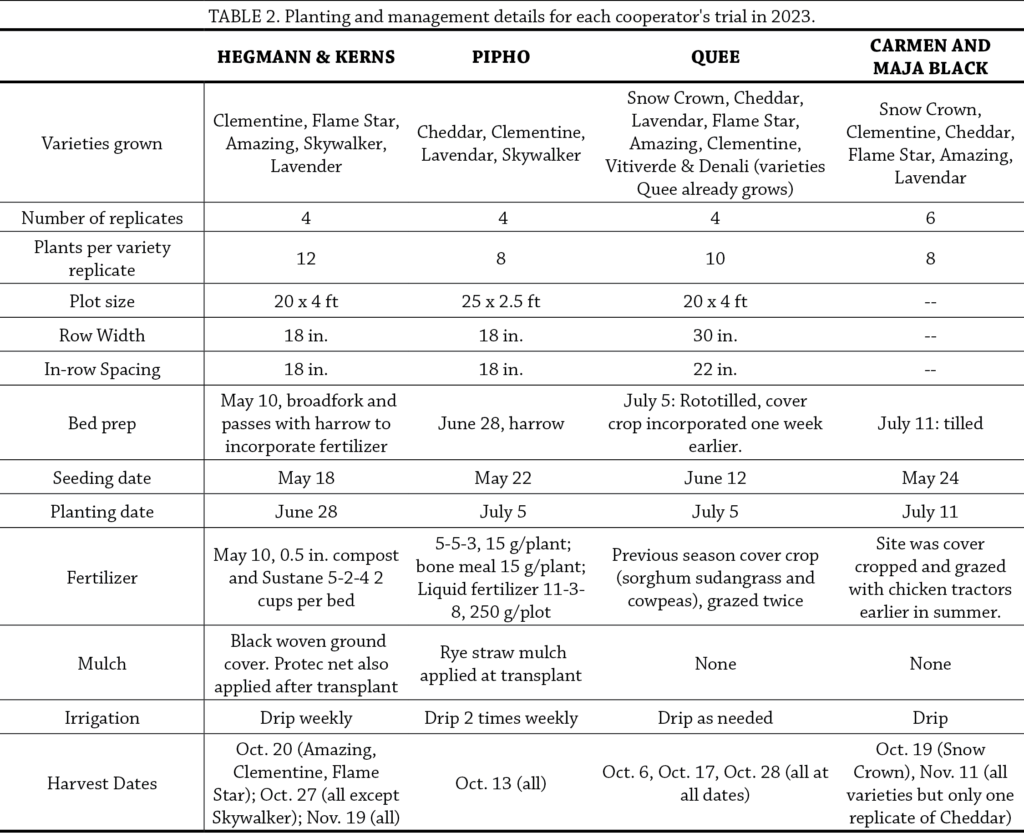
Cooperators tried the following cauliflower varieties: Snow Crown, Clementine, Cheddar, Flame Star, Amazing, Lavender, Skywalker (Table 1). Cooperators each chose varieties to grow from this list based on their individual preferences and needs (Table 2). Cooperators started seeds indoors and transplanted them in mid-to-late June on a single planting date. Each cooperator established at minimum four replicates of each selected variety; example experimental designs are shown in Figure A1. Treatment plot sizes and management details for each farm are shown in Table 2.
Measurements
At each harvest date, cooperators measured weight of all marketable heads from each plot (plot weight) and number of all marketable heads from each plot (plot count). Harvest window, average size per head, and harvest rate (heads/plant) were determined from this data. Some cooperators also counted cases of black rot and other common diseases and blemishes.
Data analysis
We used Fischer’s LSD at a 90% confidence level to determine if there were significant differences in yield between cauliflower variety. For both number of marketable heads and total marketable cauliflower weight, the difference between any two cauliflower variety yields is compared with the LSD. A difference greater than or equal to the LSD indicates the presence of a statistically significant treatment effect, meaning one treatment outperformed the other and the farmer can expect the same results to occur 90 out of 100 times under the same conditions. A difference smaller than the LSD indicates the difference is not statistically significant and the treatment had no effect. We can perform this analysis because the cooperators had completely randomized and replicated experimental designs (Figure A1).
Results and Discussion
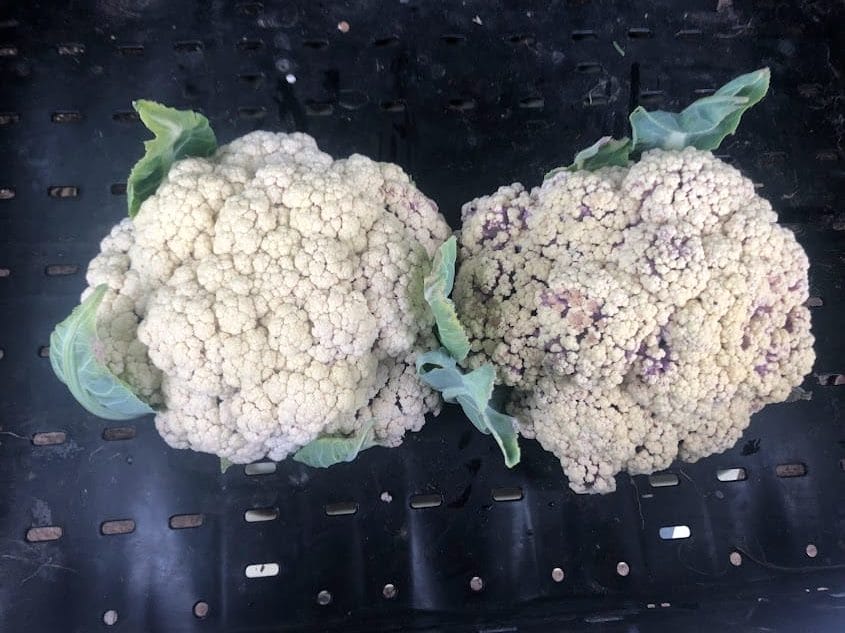

Two heads of Snow Crown cauliflower from Quee’s trial post-harvest. The head on the left is perfect for eating while the curds of the head on the right have started to separate. Photo taken October 6, 2023.
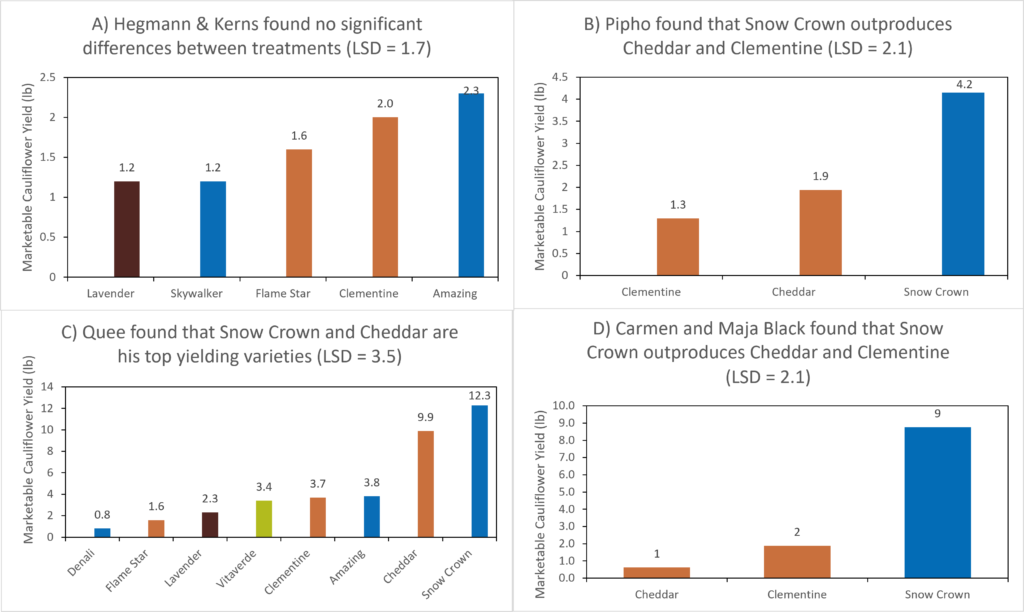
Figure 1: Weight of marketable cauliflower for each variety by farm. LSD is listed in the title of each of the four graphs. If the difference between yields of any two varieties on any given farm is greater than the LSD, those yields are considered significantly different. Click to enlarge.
All three farms that tried Snow Crown found that it outperformed most other varieties that they tested (Figure 1). Pipho found that Snow Crown yielded more than double the Clementine and Cheddar varieties he grew, and Carmen and Maja Black found that Snow Crown was the only variety she grew that consistently put out heads in all plots. At Quee’s farm, Cheddar was the only one of six varieties that yielded comparably to Snow Crown. Most cooperator’s concluded that, as shown in previous PFI trials [1,2], Snow Crown is a winning variety for getting decent yields out of fall cauliflower plantings in a variety of conditions. However, Quee notes that there are still some issues with this variety: “Snow Crown is short season and can finish in this timeframe, but I find the quality of the heads pretty poor–curd too loose and lots of purpling.”
Many cooperators were disappointed to find, once again, that the colorful orange and purple cauliflower varieties did not yield very well for fall harvest. While Cheddar yielded well at Quee’s, other colorful varieties including Clementine, Lavender and Flame Star produced very few harvestable heads on the farms that tried them. Hegmann reported, “If we do fall cauliflower again, I’d probably avoid growing the orange and purple cauliflower unless I had a ton of room.” Quee and Hegmann & Kerns also concluded that in future years they will start their fall cauliflowers two weeks earlier to give the slower growing varieties enough time to produce heads in cooler weather.
Finally, between drought, an unusually hot late summer/early fall, and broad day-to-day temperature fluctuations in the fall, the cooperators faced challenging growing conditions that affected their trials this year (Figure A2). Hardening off and keeping young transplants alive in July and August heat was difficult, with one cooperator dropping out of the trial due to transplant deaths. Pipho felt that in addition to helping him select varieties for the best fall yields, the trial was useful for him in identifying pain points with transplanting at this point in the season, and he plans on adding cauliflower to his late season product line. In contrast, the trial experience left Hegmann & Kerns convinced not to invest too much into fall cauliflower for their CSA shares: “We’ll be able to save time by focusing on more reliable (if less fun) crops, and avoid wasted expense of growing a crop that might not work out.”
Conclusions and Next Steps
As previous cooperators trials on cauliflower varieties have shown, Snow Crown consistently yields better than most other cauliflower varieties in the fall, colorful varieties tend not perform as well as farmers might want and early seeding for transplants is key to getting a successful fall cauliflower crop. While some cooperators learned that they do not want to continue investing in fall cauliflower, others now feel more confident in trying some specific varieties on a larger scale. Quee and Pipho said that in future fall cauliflower trials, they want to also investigate pest and disease resistance in different varieties.
Appendix – Trial Design and Weather Conditions
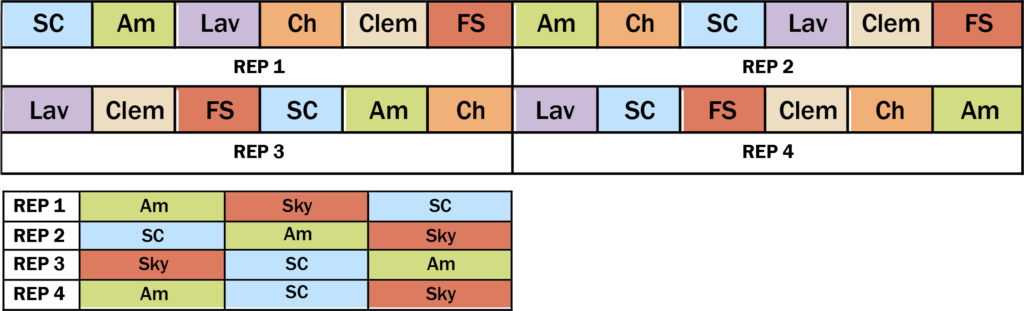
Figure A1. Examples of experimental designs used by Hegmann & Kerns, Pipho, Quee and Carmen and Maja Black.
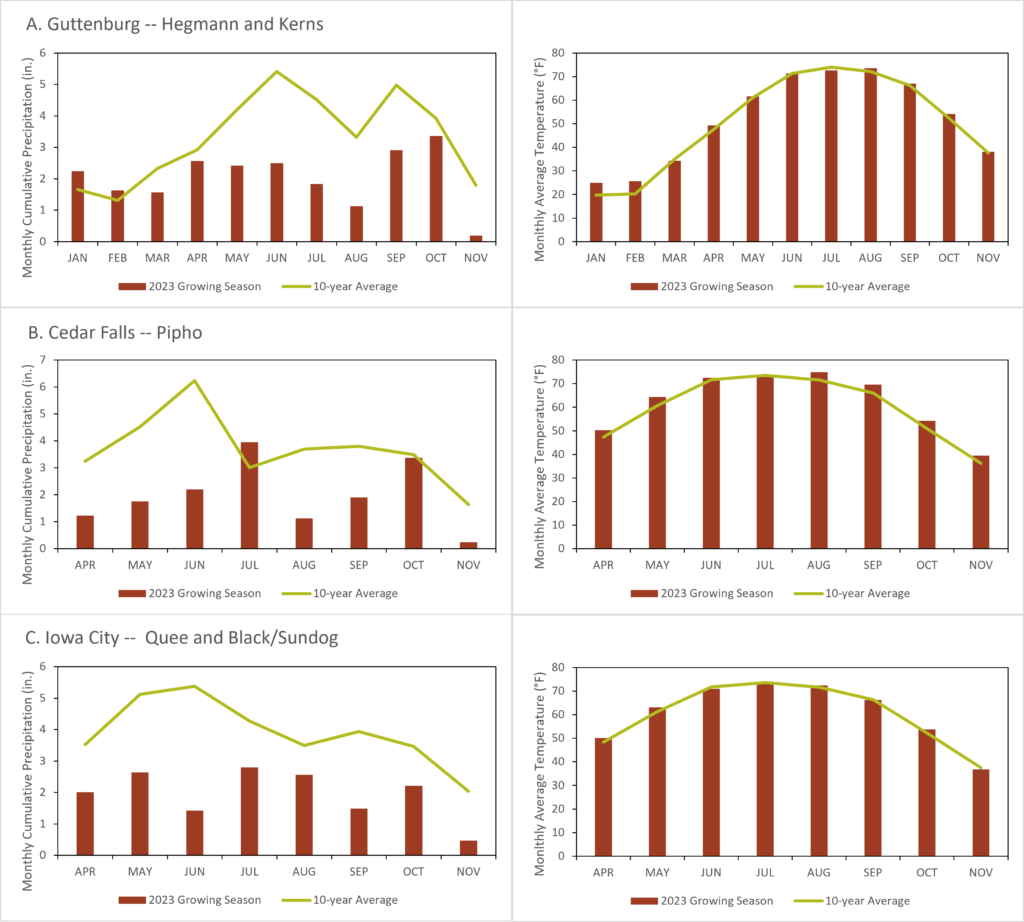
Figure A2. Weather data from the 2023 growing season and 10-year climate averages at: A) Guttenburg near Elkport (Hegmann & Kerns), B) Cedar Falls near Dunkerton (Pipho) and C) Iowa City near West Branch and Solon (Quee and Carmen and Maja Black). Left graphs show monthly precipitation accumulation in 2023 vs. 10-year normal and right graphs show monthly average temperature in 2023 vs. 10-year normal [3]. Click to enlarge.
Funding Acknowledgement
This publication or project was supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) Agricultural Marketing Service through grant 23SCBPIA1187. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the USDA.
We would also like to express our gratitude to Johnny’s Selected Seeds for donating seed for these variety trials.
References
[1] L. Kolbe, M. Quee, and S. Shellz, “Cauliflower Variety Trial,” Practical Farmers of Iowa, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://practicalfarmers.org/research/cauliflower-variety-trial/
[2] A. Carrey et al., “Fall Cauliflower Variety Trial,” Practical Farmers of Iowa, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://practicalfarmers.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/22_H-Fall-Cauliflower-variety-trial.pdf
[3] Climodat Reports, “Iowa Environmental Mesonet.” Iowa State University. [Online]. Available: http://mesonet.agron.iastate.edu/climodat/